Genetic Variation of Zinc and Iron Concentration in Normal, Provitamin A and Quality Protein Maize under Stress and Non-Stress Conditions
Abstract
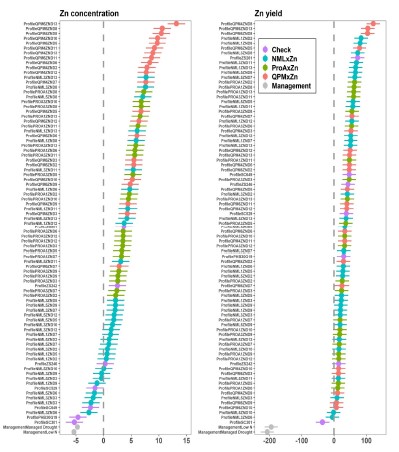
The negative impacts of zinc (Zn) and iron (Fe) deficiency due to over-reliance on monotonous cereal-based diets are well-documented. Increasing micronutrient densities in maize is currently among top breeders' priorities. Here, 77 single-cross Zn-enhanced hybrids with normal, provitamin A and quality protein maize genetic backgrounds were evaluated together with seven checks for grain Zn and Fe concentration and agronomic traits under optimum, low nitrogen (N) and managed drought conditions. Results showed a fairly wide variability for grain Zn (10.7-57.8 mg kg-1) and Fe (7.1-58.4 mg kg-1) concentration amongst the hybrids, across management conditions. Notable differences in Zn concentration were observed between the Zn-enhanced quality protein maize (QPM) (31.5 mg kg-1), Zn-enhanced provitamin A maize (28.5 mg kg-1), Zn-enhanced normal maize (26.0 mg kg-1) and checks (22.9 mg kg-1). Although checks showed the lowest micronutrient concentration, they were superior in grain yield (GY) performance, followed by Zn-enhanced normal hybrids. Genotypes grown optimally had higher micronutrient concentrations than those grown under stress. Genotype * environment interaction (G * E) was significant (p < 0.01) for GY, grain Zn and Fe concentration, hence micronutrient-rich varieties could be developed for specific environments. Furthermore, correlation between grain Zn and Fe was positive and highly significant (r = 0.97; p < 0.01) suggesting the possibility of improving these traits simultaneously. However, the negative correlation between GY and grain Zn (r = 0.44; p < 0.01) and between GY and grain Fe concentration (r = 0.43; p < 0.01) was significant but of moderate magnitude, suggesting slight dilution effects. Therefore, development of high yielding and micronutrient-dense maize cultivars is possible, which could reduce the highly prevalent micronutrient deficiency in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA).