Construction of a generalised farm typology to aid selection, targeting and scaling of onfarm research
Abstract
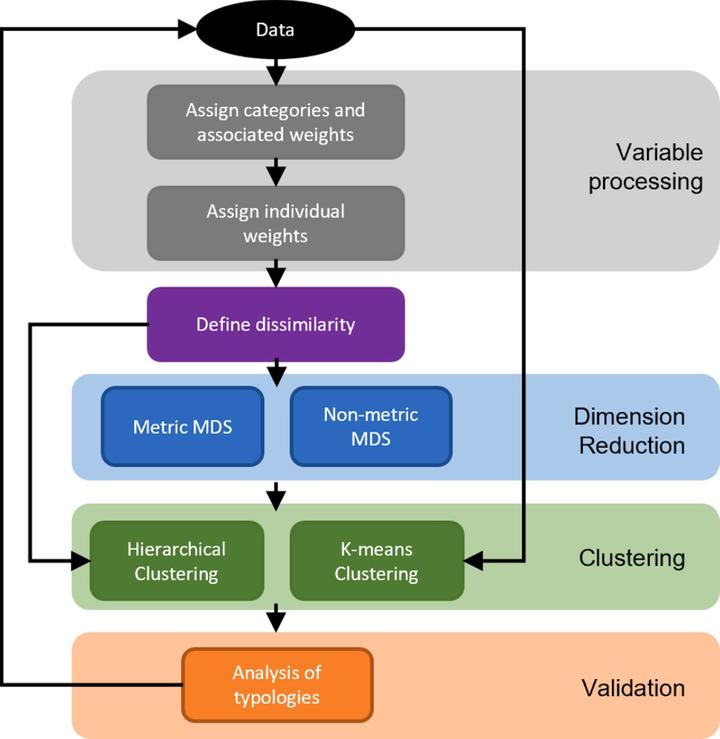
Farm typologies are often used to reduce the complexity in categorising diverse farming systems, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. The resulting typologies can then be used in multiple ways including designing efficient sampling schemes that capture the diversity in smallholder farms, prescribing the selection of certain farm types to which interventions can be targeted or upscaled, or to give context into derived relationships. However, the construction of farm typologies consists of many subjective decisions that are not always obvious or evident to the end-user. By developing a generalized framework for constructing farm typologies, we clarify where these subjective decisions are and quantify the impact they have on the resulting typologies. Further, this framework has been encapsulated in the open source RShiny App: TypologyGenerator to enable users to focus on the decisions and not the underlying implementation.